Rotating work shift schedule
Complete guide to rotationg shift schedules with examples and explanations on how they work and their benefits.
- Free rotating work shift schedule templates
- What are rotating shifts?
- Examples of common rotating shift schedules
- How to make a rotating shift schedule
- What are the benefits of rotating shifts?
- Which industries use rotating shifts?
- Legal considerations for shift scheduling
- Simplify shift scheduling with PlanningPME
- FAQ
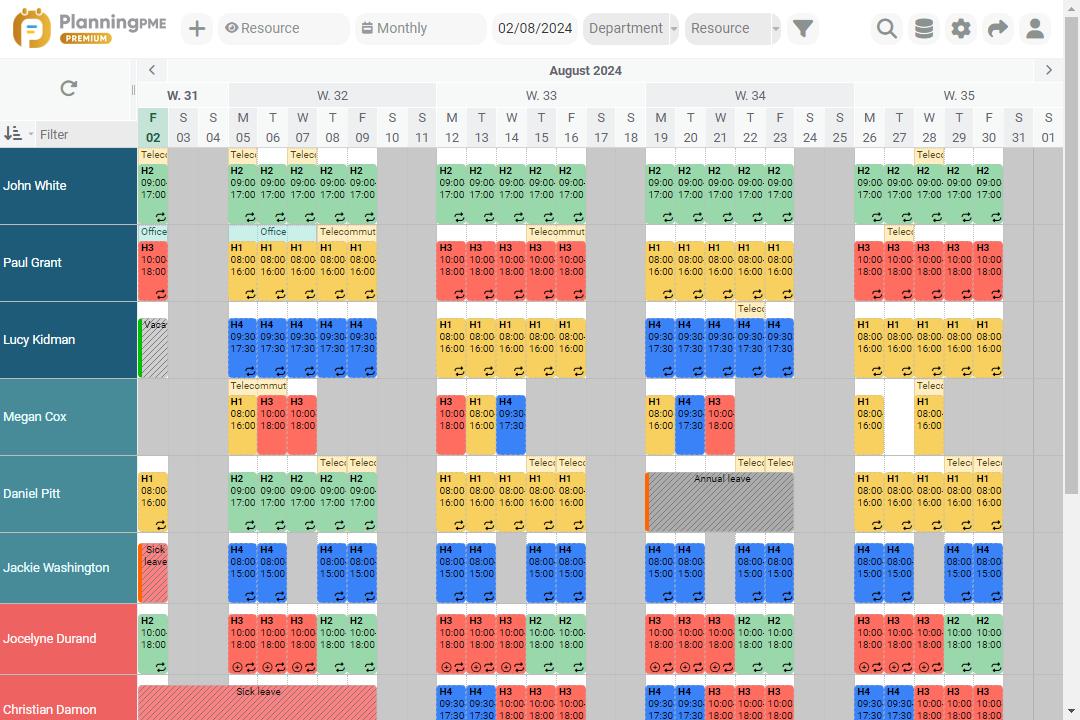
Rotating shift schedules are an essential workforce management tool for businesses operating 24/7 or with extended hours. These schedules allow employees to alternate between different shifts over a defined period, ensuring continuous operations while balancing workloads fairly. This guide explores different types of rotating shift schedules, their benefits and disadvantages, and how to implement them effectively with the work scheduling software PlanningPME.
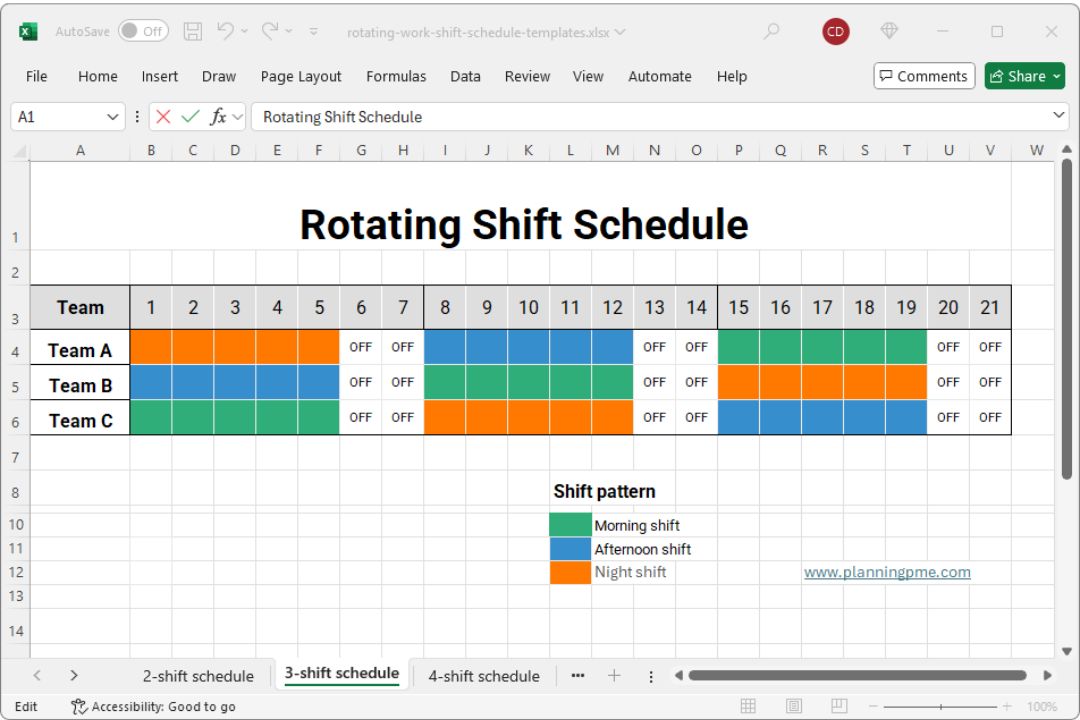
Free rotating work shift schedule templates
Whether you're looking for a quick way to get started or a more powerful tool to manage your team's shifts, you will find your solution here. You can try the PlanningPME work shift schedule template to explore a flexible and professional solution for planning shifts, or download ready-to-use Excel shift schedule templates for immediate use. Choose the option that best fits your needs.
What are rotating shifts?
Rotating shifts refer to work schedules where employees cycle through different shifts over a set period. These shifts can include morning, afternoon, evening, day and night shifts, ensuring continuous coverage for industries that require extended or 24/7 operations.
Examples of common rotating shift schedules
Rotating shifts operate on a cycle, meaning employees work specific shifts for a period and then rotate to another shift. For example, an employee may work the day shift for two weeks, switch to the night shift for two weeks, and then rotate back. This rotation ensures that all employees share the responsibility of working less desirable shifts, such as nights or weekends.
There are many different ways to create rotating shift schedules. Here are some common rotating shift schedules used in different industries.
Two-shift rotating work schedule
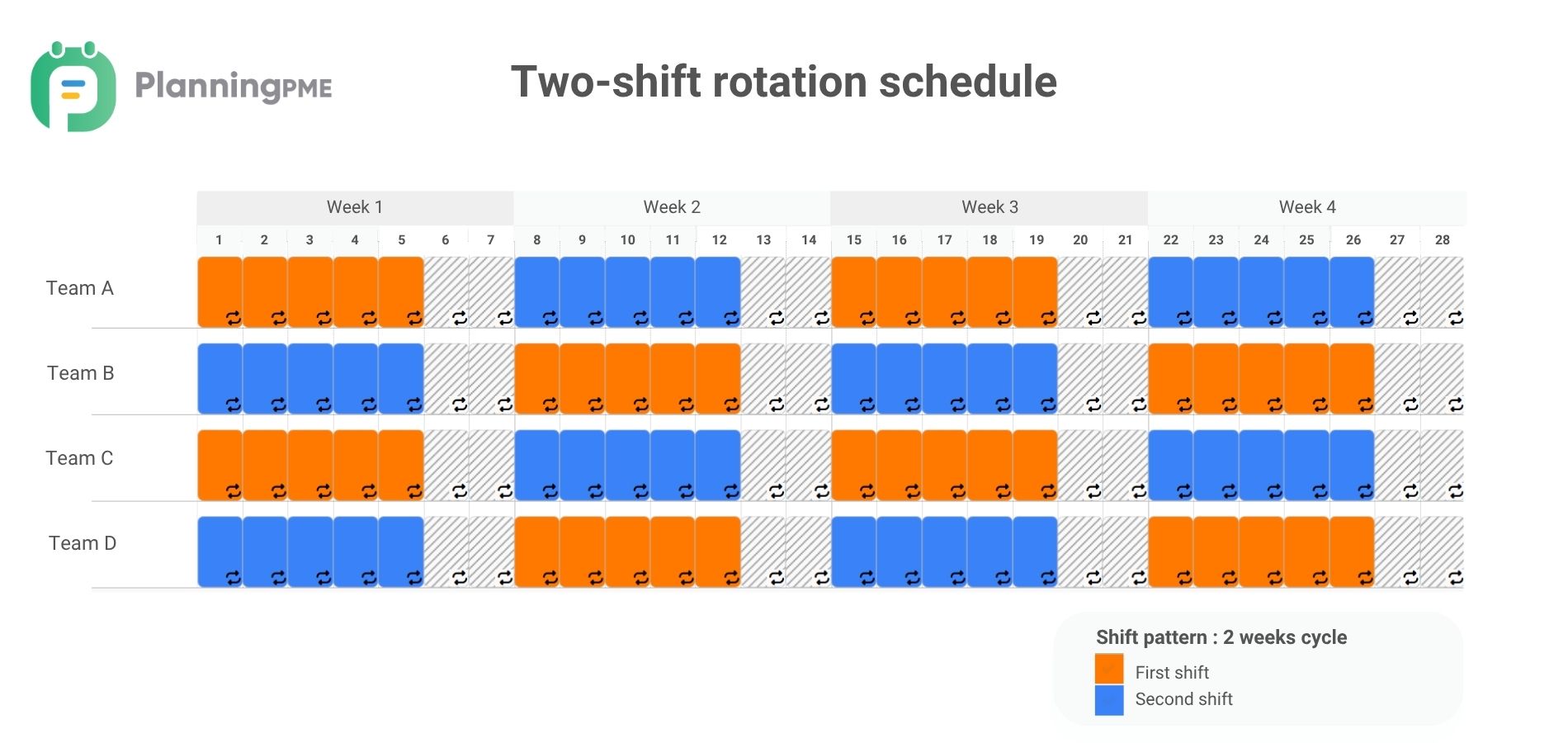
A two-shift rotating schedule divides the workday into two shifts, typically a day shift and a night shift, with each shift lasting around 8 hours. Employees rotate between the two shifts, often working a set number of days on one shift before switching to the other, ensuring continuous coverage. For example, one employee might work on the day shift the first week, then switch to the night shift the next week, creating a weekly rotation with 2 days off during the week-end.
Three-shift rotating work schedule
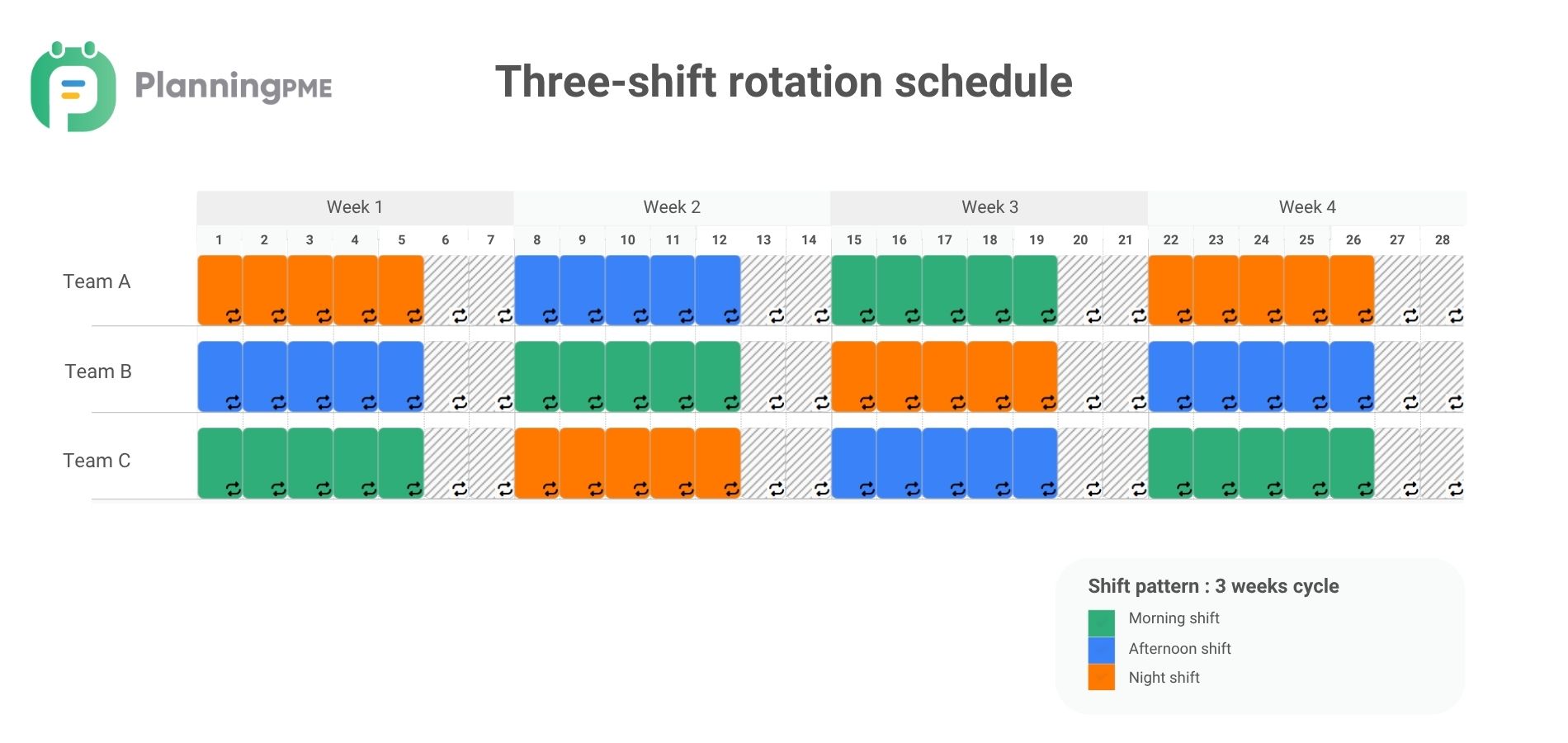
A 3-shift rotating schedule divides the workday into three shifts: morning, afternoon, and night, ensuring 24-hour coverage. Employees rotate between these shifts, typically working one week on each shift before moving to the next. For example, an employee might work the morning shift for one week, the afternoon shift the following week, and the night shift the week after, then repeating the cycle.
2-2-3 work schedule
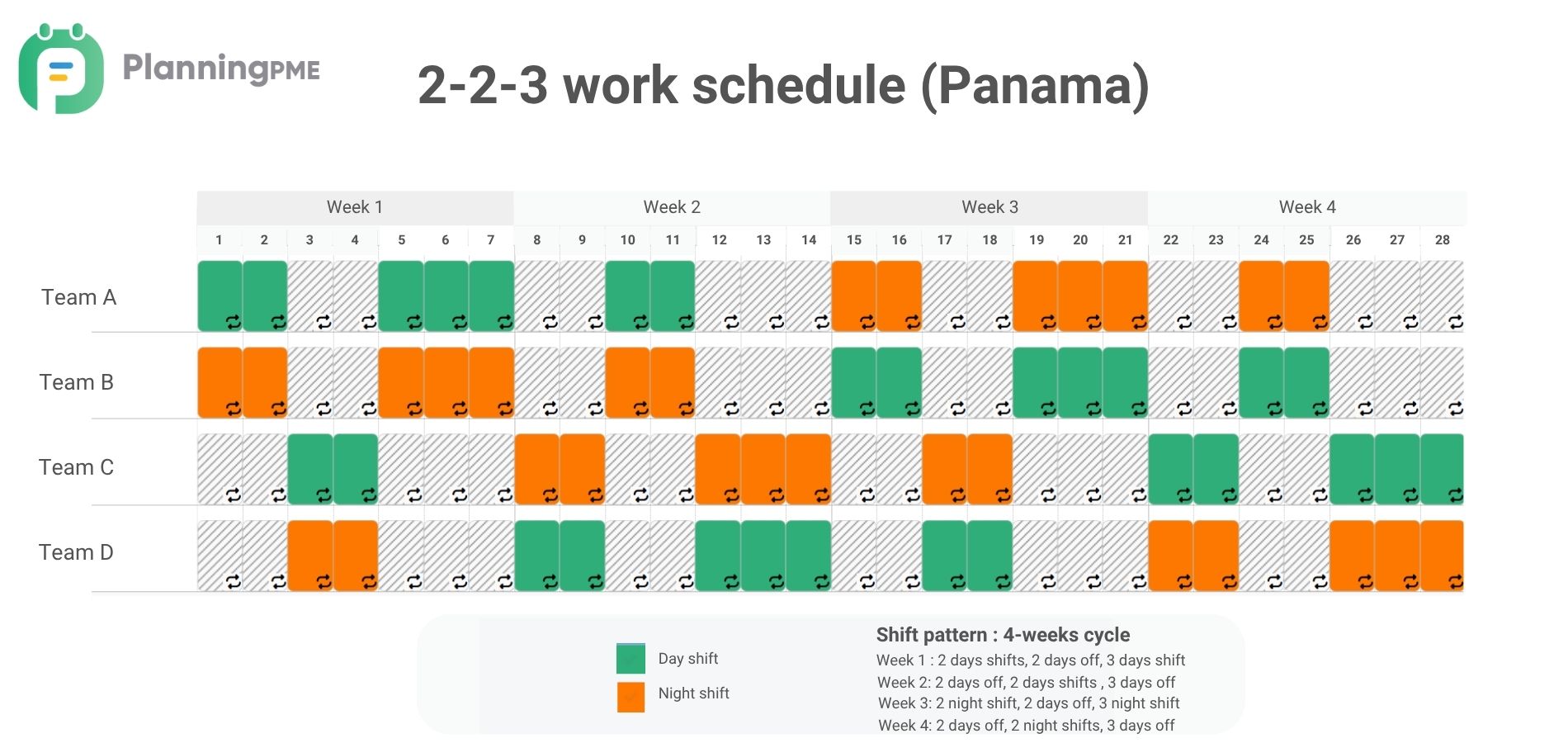
The 2-2-3 rotating work schedule also know as Panama schedule consists of employees working 2 consecutive days, followed by 2 days off, then working 3 consecutive days, and then repeating the cycle.
4-shift schedule
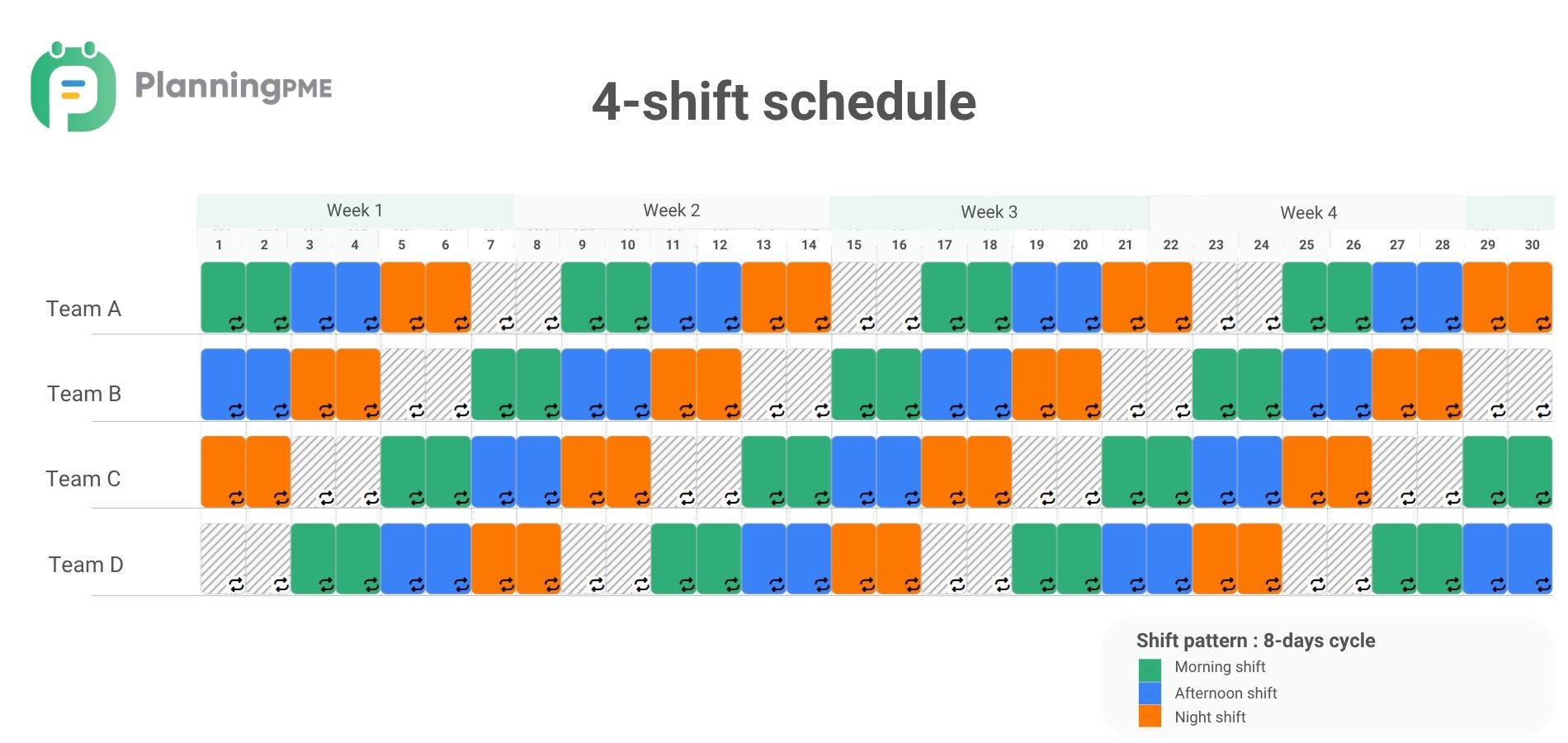
A 4-shift schedule divides the workweek into four shifts, typically covering day, afternoon, and night shifts, with a rotation pattern that ensures continuous coverage. For example, in an 8-day cycle, an employee would work day shifts for the first two days, afternoon shifts for the next two, night shifts for the next two, and then take the last two days off before starting the cycle again.
5-shift schedule

The 5*8 shift divides the working week into five teams, ensuring complete and continuous coverage of the company. For example, the rotation can follow a 10-day cycle, where employees work 2 consecutive day shifts, followed by 2 afternoon shifts, then 2 night shifts, and finally 4 days off.
4-On 4-Off shift schedule
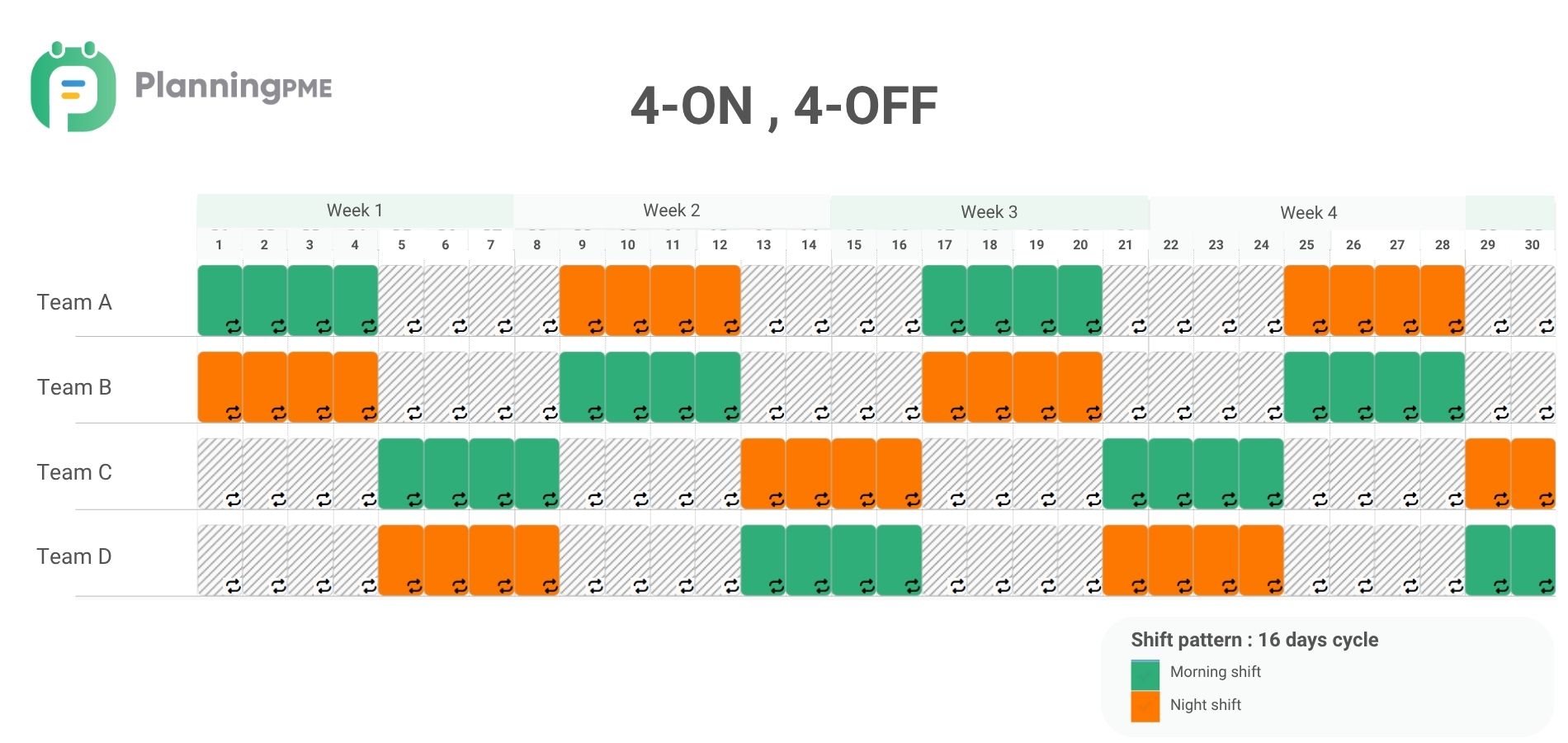
The 4-On 4-Off shift schedule involves employees working for 4 consecutive days followed by 4 days off, providing a balanced work-rest cycle.
DuPont shift schedule
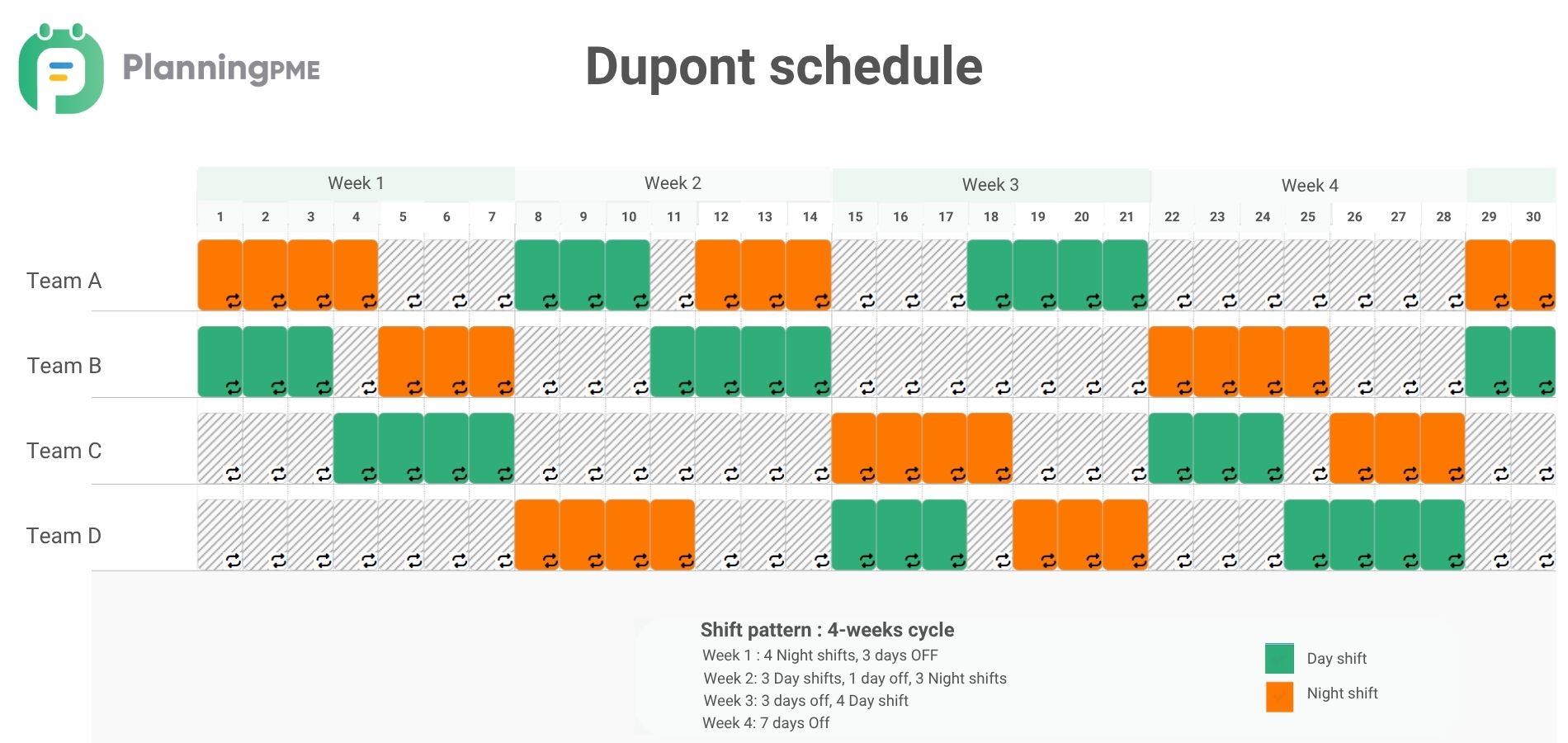
The DuPont shift schedule is a rotating 12-hour shift pattern that repeats every 4 weeks. In this shift, the work pattern of each employee is as follows: 4 days of work - 3 days off - 3 days of work - 1 day off -3 days of work -3 days off - 4 days of work - 7 days off.
How to make a rotating shift schedule
Choose a shift pattern (two-shift weekly schedule, 3-shift schedule, night-shift, etc...), and follow the steps below to create and manage a rotating shift schedule easily with PlanningPME.
1 - Define your teams and resources
Distribute employees across teams considering skills, preferences, and legal requirements.
- Teams : create teams as departments.
- Employees : Create your employees and assign them to a team. Some employees might prefer to work certain shifts (day/afternoon/night).
2 - Define the time profile of each employee
Define the number of hours that should be counted each day on the default profile. Note that default profile is assigned by default to all employees.
- Default weekly profile : From the Data menu -> Timetable, open the default profile, select "Number of hours" for "Work capacity relying on" and specify the days of work and number of working hours/day (e.g. Mon-Fri, 8 hours/day).
- Special profiles : From the Data menu -> Timetable, create other profiles for employees with special weekly hour profiles (half-week, morning only, etc…). Then, from the "Timetable" tab of the resource card, you can assign specific profiles to resources individually.
3 - Create your shifts using "tasks"
Create your different shifts as "tasks" from the Data menu -> Task (e.g. morning, day and night shifts).
- Label : This will be the name of the shift (e.g. “Morning shift”, “9h00-17h00”)
- Colour : Assign a colour to each shift to differentiate the shifts visually.
4 - Create your list of leaves and time-offs
Create a list of your leaves and time-offs from the Data menu-> Unavailability.
- Label : Name of the unavailability (e.g. annual leave, special leave, PTO)
- Colour : Select a colour for each unavailability. Note that unavailabilities are displayed with hatchings on the schedule to differentiate from tasks.
5 - Create all recurring shifts
To create the shifts, start by defining the logic of the rotating cycle pattern: frequency (daily, weekly, etc.), start date, and end date. You can easily create your full schedule even for the entire year.
6 - Adjust the schedule as needed
With PlanningPME, you can reassign the shifts easily as needed, for exemple, when an employee is on an annual leave. All the changes to the schedule are recorded in the history log, so that you will be able to track who changed what when necessary.
7 - Communicate and share the schedule
You can communicate and share the schedule to everyone concerned. The following functionalities will help a seamless communication in real-time:
- Limited or read-only access : Give each user an access to the schedule with specific limitations as to what they can see and modify.
- Notifications : Send notifications automatically to people concerned, triggered by the actions that you specify (e.g. modification of a task, leave request)
- Calendar synchronisation : Synchronise your PlanningPME schedule with calendar applications such as Google Calendar or Outlook so that the information on PlanningPME is also visible in these applications.
8 - Extract number of hours worked for each employee
You can create reports on the number of hours worked for a set period (per week, month, year, etc) for each employee.
- Excel reports/ pivot table : Create your own pivot table reports of the hours worked by employees each week, month or year and update them regularly.
- Integration/ API : Integrate your schedule with your time recording software
What are the benefits of rotating shifts?
Rotating shifts offer key advantages for businesses and employees, ensuring continuous operations and balanced workloads.
- Better coverage : Maintains extended operations with fair workload distribution.
- Skills development : Enhances adaptability, problem-solving, and versatility through varied shift experiences.
- Fairness and well-being : Reduces fatigue by sharing night shifts and promoting healthier schedules.
- Increased engagement : Prevents monotony, keeping employees motivated and productive.
- Work-life balance : Offers flexibility for personal time, errands, and social activities.
- Lower overtime costs : Reduces the need for overtime, minimising labour costs and employee burnout.
- Adaptability : Prepares employees to respond quickly to unexpected demands, ensuring operational efficiency.
A well-planned rotating shift system enhances productivity, fairness, and employee satisfaction, contributing to a resilient and successful workforce.
Which industries use rotating shifts?
Industries that commonly use rotating shifts include:
- Healthcare : Hospitals, clinics, and emergency services requiring 24/7 staffing.
- Manufacturing : Factories and production plants that need continuous operation.
- Emergency services : Police, fire departments, and paramedics working in shifts for round-the-clock availability.
- Transportation : Airlines, shipping, railways, and public transport services operating all hours.
- Hospitality : Hotels, restaurants, and customer service centers.
- IT and data centers : Technology support and data monitoring requiring staff availability at all times.
These industries benefit from rotating shifts by ensuring constant service, maximising efficiency, and balancing employee workloads.
Legal considerations for shift scheduling
When creating shift schedules, it is essential to comply with labour laws, including regulations on maximum working hours, rest periods, overtime pay, and employee rights.
- Comply with labour laws on work hours and rest periods
- Provide adequate breaks to prevent tiredness
- Train employees on health management during shift work
Adhering to legal guidelines not only protects businesses from penalties but also ensures fair treatment and well-being of employees.
Simplify shift scheduling with PlanningPME
Rotating shifts enhance operational continuity but require careful planning to balance productivity and employee well-being. PlanningPME makes it easy to create and manage any shift pattern thanks to its recurrent event feature. Whether you need rotating shifts, fixed schedules, or complex 24/7 coverage, the software automates recurring shifts to save time and reduce errors. Users can set up patterns such as weekly rotations, alternating shifts, or custom cycles with just a few clicks. This flexibility ensures that schedules remain clear, organised, and compliant with labour regulations. With PlanningPME, businesses can efficiently handle workforce planning while ensuring fairness and productivity.
FAQ
Rotating shift schedules can improve productivity by providing continuous coverage, while ensuring that employees are well-rested and performing at their peak during their assigned shifts. However, too much rotation without proper rest can lead to tiredness and reduced performance, so balance is important.
Rotating shifts can have both positive and negative effects on health. While they offer flexibility and better work-life balance, they can disrupt circadian rhythms, leading to fatigue, sleep disturbances, and increased stress if not managed properly.
The main challenges for employees working rotating shifts include difficulty in maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, fatigue and stress, and potential disruptions in social life. These issues can be mitigated with proper rest, support, and adjustments to the schedule.
Yes, rotating shift schedules can be customised based on employee preferences, skill sets, or roles within the company. Many employers aim to provide flexibility by allowing employees to request specific shifts or patterns, ensuring that both the company and the employees are satisfied with the arrangement.
Effective communication is key when managing shift changes in rotating schedules. The use of scheduling software or systems can help automate the process, allowing employees to easily view and swap shifts. Regular discussions with employees can also ensure that the system is working smoothly.